Symptoms of Common Eye Diseases
Our eyes are one of the most important aspects of our bodies, allowing us to experience and interact with the world around us. Yet, despite their importance, they are often taken for granted until problems arise.
Eye diseases can develop gradually, sometimes with little to no warning signs, and can lead to significant vision impairment if left untreated. Understanding these conditions and how to prevent them is essential for maintaining lifelong eye health.
In what follows, we will explore some of the most common eye diseases, including cataracts, glaucoma, age-related macular degeneration, and more. We will discuss the symptoms to watch for, as well as practical steps you can take to protect your vision.
Common Eye Diseases
Our eyes are complex organs, susceptible to various diseases impacting vision and overall eye health. Understanding these conditions is an important part of early detection and treatment. The following are some of the most common eye diseases, along with their definitions and symptoms:
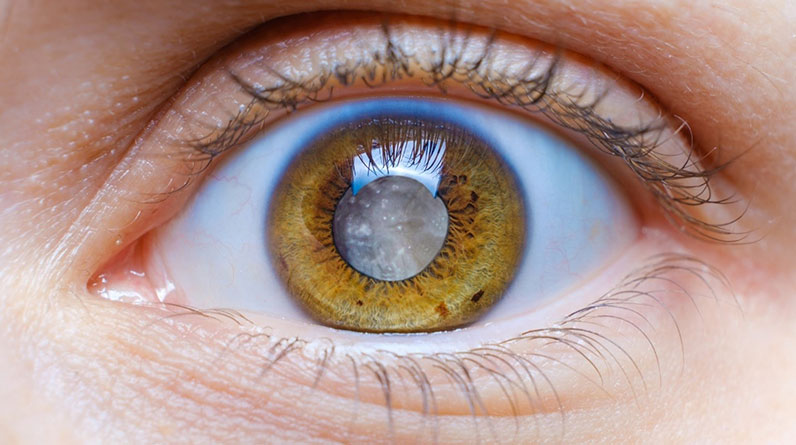
1. Cataracts
A cataract is the clouding of the eye’s natural lens, which lies behind the iris and the pupil. It is primarily associated with aging but can also result from trauma, certain medications, or other medical conditions.
Symptoms:
- Blurred or cloudy vision
- Sensitivity to light and glare
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Fading or yellowing of colors
- Double vision in one eye
2. Glaucoma
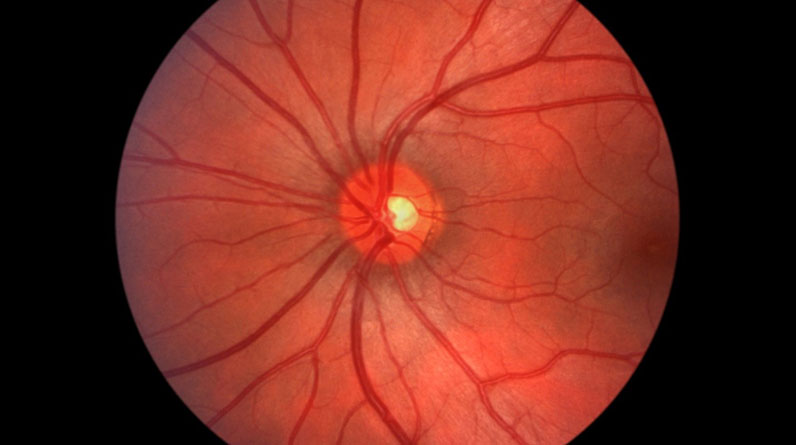
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve, often due to abnormally high pressure in the eye. It is a leading cause of blindness, particularly in older adults.
Symptoms:
- Gradual loss of peripheral vision, usually in both eyes
- Tunnel vision in advanced stages
- Severe eye pain (in acute cases)
- Halos around lights
- Redness in the eye
- Nausea or vomiting (in acute cases)
3. Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
AMD is a degenerative disease that affects the macula, the part of the retina responsible for central vision. It is most common in older adults and is a leading cause of vision loss.
Symptoms:
- Blurred or reduced central vision
- Difficulty recognizing faces
- Straight lines appearing wavy
- Need for brighter light when reading or doing close work
- Difficulty adjusting to low light levels
4. Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that affects the retina’s blood vessels. Over time, it can lead to vision impairment and blindness if not managed properly.
Symptoms:
- Spots or dark strings floating in your vision (floaters)
- Blurred vision
- Fluctuating vision
- Impaired color vision
- Dark or empty areas in your vision
- Vision loss
5. Dry Eye Syndrome
Dry Eye Syndrome occurs when your eyes don’t produce enough tears or the right quality of tears to keep the eyes lubricated. It can cause discomfort and vision problems.
Symptoms:
- Stinging, burning, or scratchy sensation in the eyes
- Sensitivity to light
- Redness of the eyes
- A sensation of having something in your eyes
- Difficulty wearing contact lenses
- Difficulty with nighttime driving
- Watery eyes (body’s response to irritation)
6. Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye)
Conjunctivitis is the inflammation or infection of the conjunctiva, the thin transparent layer of tissue covering the eye’s white part. It is highly contagious and can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or allergens.
Symptoms:
- Redness in one or both eyes
- Itchiness in one or both eyes
- A gritty feeling in one or both eyes
- A discharge that forms a crust during the night
- Tearing
These common eye diseases can significantly impact vision and quality of life. Early detection through regular eye exams is the pathway to managing these conditions effectively.
Prevention of Eye Diseases
Preventing eye diseases is necessary for maintaining good vision and overall eye health. While some eye conditions are unavoidable due to factors like aging or genetics, there are several steps you can take to reduce the risk of developing eye diseases.
Here’s how:
1. Importance of Regular Eye Exams
Regular eye exams are the main way to prevent eye disease. Many eye conditions, such as glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy, develop gradually and may not show noticeable symptoms in the early stages. An eye exam can detect these conditions before they progress, allowing for early intervention and better outcomes.
What to Do:
- Schedule comprehensive eye exams every one to two years or as recommended by your eye care professional.
- Ensure that your exams include tests for eye pressure, visual acuity, and retinal health.
2. Wearing Sunglasses
Exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays can increase the risk of developing cataracts, macular degeneration, and other eye conditions. Sunglasses that block 100% of UV rays are essential for protecting your eyes from these harmful effects.
What to Do:
- Choose sunglasses that offer 100% UVA and UVB protection.
- Wear sunglasses even on cloudy days, as UV rays can penetrate clouds.
- Consider wearing a wide-brimmed hat for additional protection.
3. Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
A healthy lifestyle plays a significant role in eye disease prevention. Proper nutrition, regular exercise, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking can help keep your eyes healthy.
What to Do:
- Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids. Foods like spinach, kale, carrots, and fish are excellent for eye health.
- Exercise regularly to maintain healthy blood circulation, which is vital for eye health.
- Avoid smoking, as it increases the risk of developing cataracts, AMD, and other eye conditions.
- Manage chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension, which can lead to eye diseases if left uncontrolled.
4. Maintaining Hygiene to Prevent Infections
Eye infections, such as conjunctivitis (pink eye), can be prevented by practicing good hygiene. This is particularly important if you wear contact lenses, as improper care can lead to serious eye infections.
What to Do:
- Wash your hands thoroughly before touching your eyes or handling contact lenses.
- Avoid touching or rubbing your eyes, especially with unclean hands.
- Disinfect contact lenses as directed by your eye care provider and replace them according to the schedule provided.
- Avoid sharing personal items like towels, makeup, or eye drops, which can spread infections.
Taking care of your eyes is important for preserving your vision and overall quality of life. By understanding common eye diseases and recognizing their symptoms early, you can seek timely treatment and prevent potential complications.